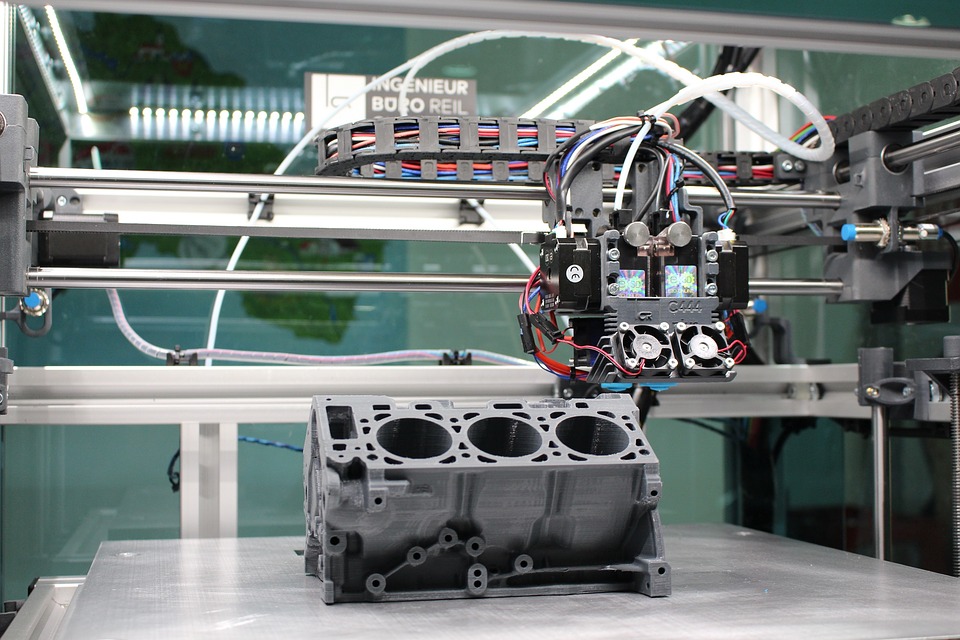
If you’re involved in product development or you’re an entrepreneur who wants to look into having an idea developed into a product, there’s a lot to learn. One term you should be aware of is rapid prototyping, which is important in custom manufacturing and prototyping in general.
The following is a guide to rapid prototyping, including the benefits of the process.
What Is Rapid Prototyping?
When it comes to manufacturing and automation, rapid prototyping is valuable in many ways. The term rapid prototyping refers to an agile strategy using in product development.
With rapid prototyping, it becomes possible to create a 3D prototype of a product, and then that can be used for the optimization of said product.
Rapid prototypes are created with the use of simulations, and many different versions of the product can be produced during a short time. Each iteration of the product can integrate changes based on feedback.
Rapid prototyping is known more commonly as 3D printing, which is part of automated manufacturing technology.
A rapid prototype doesn’t have the full functionality of the final product, but it can look so much like what the product will look like that it can be used as a foundation for analysis and feedback.
How Does Rapid Prototyping Work?
With rapid prototyping, in most cases, there is a virtual design made using a computer-aided design or CAD software. Then, once there is a design in CAD or some other modeling software, a printing machine takes the data and then uses layers of material, which can be sheet material or a liquid or powder.
The physical prototype is built through cross-sections and layers. These sections are joined together automatically, and then you receive the shape of the product.
In most situations, rapid prototyping technology can mean you have a 3D model in just a few hours, but not always.
A rapid prototype can indicate that you’re on the right track for your product development. On the other hand, it can also show that a lot of work still needs to be done.
A rapid prototype model can be used in conjunction with wireframes to show what the user experience (UX) might be like.
What Are the Benefits of Rapid Prototyping?
If you’re not sure if rapid prototyping is a good option for your product development process, it’s worth considering the potential pros and cons. First, the benefits of rapid prototyping include the fact that it’s a way to experiment with your idea in a safe environment.
You have more options, and you’ve invested much less in terms of time and money if you can see a rapid prototype and perhaps determine it won’t work, or that it will work with significant changes.
Essentially, you can take a rapid prototype and completely scrap it if you need to.
Using a prototype can encourage creativity, problem-solving and out-of-the-box thinking that can lead to a much better product overall. This will mean when your product goes to market, it’s going to be more competitive.
There is minimal waste that goes along with the use of CAD software and 3D printing, and you can minimize design flaw while completely customizing your design.
Are There Disadvantages of Prototyping?
As with anything, there are disadvantages to prototyping, although they’re fairly minimal. One of the possible disadvantages of prototyping is that developers might not be able to analyze what the final product will fully look like.
Also, if you’re using a prototype as something to show to a customer, it can be confusing for them. They may be unhappy because they don’t realize that it’s a rough model of what the product will actually look like. A customer may also start to have an affinity for the prototype, which could lead to confusion or disappointment when it’s time for the actual product.
While prototypes are intended to save time, with rapid prototyping, it can turn into something that leads to delays. There can be so much input, brainstorming, and back and forth that it ends up slowing the entire timeline down.
Finally, a prototype does little to highlight how the product will be used. As was touched on, some of this can be alleviated through the use of wireframes with some products, but not always. Overall, the option to use rapid prototyping and automation can prove valuable in the development process, as long as attention is given to possible downsides as well.